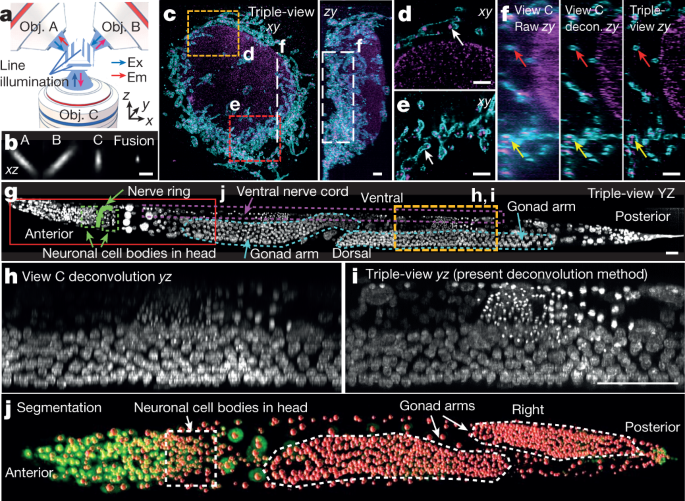
1.Pawley, J. B. (ed.) Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy 3rd edn (Springer, 2006).2.Laissue, P. P., Alghamdi, R. A., Tomancak, P., Reynaud, E. G., Shroff, H. Assessing phototoxicity in live fluorescence imaging. Nat. Methods 14, 657–661 (2017).CAS Article Google Scholar 3.Baumgart, E. & Kubitscheck, U. Scanned light sheet microscopy with confocal slit detection. Opt. Express 20, 21805–21814 (2012).ADS Article Google Scholar 4.Kumar, A. et al. Using stage- and slit-scanning to improve contrast and optical sectioning in dual-view inverted light-sheet microscopy (diSPIM). Biol. Bull. 231, 26–39 (2016).CAS Article Google Scholar 5.Guo, M. et al. Rapid image deconvolution and multiview fusion for optical microscopy. Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 1337–1346 (2020).CAS Article Google Scholar 6.Lucy, L. B. An iterative technique for the rectification of observed distributions. Astron. J. 79, 745–754 (1974).ADS Article Google Scholar 7.Richardson, W. H. Bayesian-based iterative method of image restoration. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 62, 55–59 (1972).ADS Article Google Scholar 8.Descloux, A., Grußmayer, K. S. & Radenovic, A. Parameter-free image resolution estimation based on decorrelation analysis. Nat. Methods 16, 918–924 (2019).CAS Article Google Scholar 9.Chen, F., Tillberg, P. & Boyden, E. S. Expansion microscopy. Science 347, 543–548 (2015).ADS CAS Article Google Scholar 10.He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollár, P. & Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In 2017 IEEE Conf. Computer Vision (ICCV) (eds Ikeuchi, K. et al.) 2980–2988 (2017).11.Lin, T.-Y. et al. Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In Computer Vision – CCV 2014 (eds Fleet, D. et al.) 740–755 (Springer, 2014).12.Kosmach, A. et al. Monitoring mitochondrial calcium and metabolism in the beating MCU-KO heart. Cell Rep. 37, 109846 (2021).13.Wu, Y. et al. Inverted selective plane illumination microscopy (iSPIM) enables coupled cell identity lineaging and neurodevelopmental imaging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 17708–17713 (2011).ADS CAS Article Google Scholar 14.Weigert, M. et al. Content-aware image restoration: pushing the limits of fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Methods 15, 1090–1097 (2018).CAS Article Google Scholar 15.Sulston, J. E., Schierenberg, E., White, J. G. & Thomson, J. N. The embryonic cell lineage of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 100, 64–119 (1983).CAS Article Google Scholar 16.Wu, Y. et al. Spatially isotropic four-dimensional imaging with dual-view plane illumination microscopy. Nat. Biotechnol. 31, 1032–1038 (2013).CAS Article Google Scholar 17.Kumar, A. et al. Dual-view plane illumination microscopy for rapid and spatially isotropic imaging. Nat. Protoc. 9, 2555–2573 (2014).CAS Article Google Scholar 18.Duncan, L. H. et al. Isotropic light-sheet microscopy and automated cell lineage analyses to catalogue Caenorhabditis elegans embryogenesis with subcellular resolution. J. Vis. Exp. 148, e59533 (2019). Google Scholar 19.Towlson, E. K., Vértes, P. E., Ahnert, S. E., Schafer, W. R. & Bullmore, E. T. The rich club of the C. elegans neuronal connectome. J. Neurosci. 33, 6380–6387 (2013).CAS Article Google Scholar 20.White, J. G., Southgate, E., Thomson, J. N. & Brenner, S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 314, 1–340 (1986).ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar 21.Armenti, S. T., Lohmer, L. L., Sherwood, D. R. & Nance, J. Repurposing an endogenous degradation system for rapid and targeted depletion of C. elegans proteins. Development 141, 4640–4647 (2014).CAS Article Google Scholar 22.Wu, Y. & Shroff, H. Faster, sharper, and deeper: structured illumination microscopy for biological imaging. Nat. Methods 15, 1011–1019 (2018); correction 16, 205 (2019).CAS Article Google Scholar 23.Fischer, R. S., Gardel, M. L., Ma, X., Adelstein, R. S. & Waterman, C. M. Local cortical tension by myosin II guides 3D endothelial cell branching. Curr Biol. 19, 260–265 (2009).CAS Article Google Scholar 24.York, A. G. et al. Instant super-resolution imaging in live cells and embryos via analog image processing. Nat. Methods 10, 1122–1126 (2013).CAS Article Google Scholar 25.Gambarotto, D. et al. Imaging cellular ultrastructures using expansion microscopy (U-ExM). Nat. Methods 16, 71–74 (2019).CAS Article Google Scholar 26.Tabara, H., Motohashi, T. & Kohara, Y. A multi-well version of in situ hybridization on whole mount embryos of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 2119–2124 (1996).CAS Article Google Scholar 27.Chen, J. et al. Three-dimensional residual channel attention networks denoise and sharpen fluorescence microscopy image volumes. Nat. Methods 18, 678–687 (2020).Article Google Scholar 28.Wu, Y. et al. Simultaneous multiview capture and fusion improves spatial resolution in wide-field and light-sheet microscopy. Optica 3, 897–910 (2016).ADS CAS Article Google Scholar 29.Barth, R., Bystricky, K. & Shaban, H. A. Coupling chromatin structure and dynamics by live super-resolution imaging. Sci. Adv. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz2196 (2020).Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar 30.Han, X. et al. A polymer index-matched to water enables diverse applications in fluorescence microscopy. Lab Chip 21, 1549–1562 (2021).CAS Article Google Scholar 31.Chen, B.-C. et al. Lattice light-sheet microscopy: imaging molecules to embryos at high spatiotemporal resolution. Science 346, 1257998 (2014).Article Google Scholar 32.Gustafsson, M. G. L. et al. Three-dimensional resolution doubling in wide-field fluorescence microscopy by structured illumination. Biophys. J. 94, 4957–4970 (2008).ADS CAS Article Google Scholar 33.Rego, E. H. et al. Nonlinear structured-illumination microscopy with a photoswitchable protein reveals cellular structures at 50-nm resolution. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, E135–E143 (2011).Article Google Scholar 34.Krüger, J.-R., Keller-Findeisen, J., Geisler, C. & Egner, A. Tomographic STED microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 11, 3139–3163 (2020).Article Google Scholar 35.Wu, Y. et al. Reflective imaging improves spatiotemporal resolution and collection efficiency in light sheet microscopy. Nat. Commun. 8, 1452 (2017).ADS Article Google Scholar 36.Shroff, H., York, A., Giannini, J. P. & Kumar, A. Resolution enhancement for line scanning excitation microscopy systems and methods. US patent 10,247,930 (2019).37.Wang, H. et al. Deep learning enables cross-modality super-resolution in fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Methods 16, 103–110 (2019).CAS Article Google Scholar 38.Ji, N. Adaptive optical fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Methods 14, 374–380 (2017).CAS Article Google Scholar 39.Royer, L. A. et al. Adaptive light-sheet microscopy for long-term, high-resolution imaging in live organisms. Nat. Biotechnol. 34, 1267–1278 (2016).CAS Article Google Scholar 40.Liu, T.-L. et al. Observing the cell in its native state: imaging subcellular dynamics in multicellular organisms. Science 360, eaaq1392 (2018).ADS Article Google Scholar 41.Zheng, W. et al. Adaptive optics improves multiphoton super-resolution imaging. Nat. Methods 14, 869–872 (2017).CAS Article Google Scholar Page 2 Full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of illumination (first row) and FWHM derived from images of 100-nm diameter beads in x, y, z direction (latter rows) at different subregions of imaging field (#1–#9); n = 15 measurements were used to derive means ± standard deviations for each entry, all units in nm.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04110-0
Multiview confocal super-resolution microscopy